For results for completed and on-going clinical trials in ovarian cancer for all drugs in a specific category, click on the drug category (e.g., Angiogenesis Inhibitors) on the left. To see only results for specific drugs in a class, click on the drug class for the drugs that interest you. For a schematic diagram of cell growth and survival pathways that these drugs inhibit, please scroll to the bottom of the page.
| DNA DAMAGE REPAIR PATHWAY INHIBITORS | PARP Inhibitors | Niraparib (Zejula™) Olaparib (Lynparza™) Pamiparib Rucaparib (Rubraca™) Talazoparib (Talzenna™) Veliparib |
|---|---|---|
| ATR Inhibitors | Berzosertib |
| ANTIBODY TARGETED DRUG CONJUGATES | Antibody Drug Conjugates (ADC)
Targeting B7H4, CDH6, CLDN6, FRalpha, HER2, TROP2 |
AZD5335 Datopotamab deruxtecan (Dato-Dxd) Farletuzumab ecteribulin Felmetatug vedotin (SGN-B7H4) Luveltamab tazevibulin (STRO-002) Mirvetuximab soravtansine (Elahere™) Puxitatug samrotecan (AZD8205) Raludotatug deruxtecan (R-Dxd) Rinatabart sesutecan (Rina-S) Sacituzumab tirumotecan (Sac-TMT) TORL-1-23 Trastuzumab deruxtecan (Enhertu™) |
|---|
| ANGIOGENESIS and GROWTH FACTOR/ RECEPTOR INHIBITORS | VEGF, DLL4 Antagonists | Bevacizumab (Avastin™) Dilpacimab Navicixizumab |
|---|---|---|
| VEGFR Inhibitors | Cediranib | |
| Multi-targeted RTK Inhibitors | Anlotinib Lenvatinib (Lenvima™) Pazopanib (Votrient™) Rebastinib Sitravatinib Sorafenib |
|
| Gas6 Antagonists | Batiraxcept |
| HORMONAL THERAPY | Aromatase Inhibitors | Anastrozole (Arimidex™) Letrozole (Femara™) |
|---|---|---|
| Anti Estrogens | Tamoxifen (Nolvadex™) | |
| ER Antagonists | Fulvestrant (Faslodex™) | |
| GR Antagonists | Relacorilant |
| SIGNALING PATHWAY INHIBITORS | Integrins/FAK Pathway
Targeting FAK |
Defactinib |
|---|---|---|
| PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway
Targeting AKT, PI3Kalpha, pan-PI3K, mTOR, TORC1/2 |
Afuresertib Alpelisib (Piqray™) Buparlisib Capivasertib Everolimus (Afinitor™) Metformin Temsirolimus (Torisel™) Vistusertib |
|
| RAS/RAF/MAPK Pathway
Targeting RAF, MEK |
Avutometinib Binimetinib (Mektovi™) Selumetinib (Koselugo™) Trametinib (Mekinist™) |
|
| JAK/STAT Pathway Targeting Stat3 |
Napabucasin |
| CELL CYCLE INHIBITORS | AURK Inhibitors | Alisertib |
|---|---|---|
| CDK4/6 Inhibitors | Abemaciclib (Verzenio™) Palbociclib (Ibrance™) Ribociclib (Kisqali™) |
|
| CHK1/2 Inhibitors | ACR-368 | |
| p53 Activators | Eprenetapopt | |
| Wee1 Inhibitors | Adavosertib Azenosertib |
| IMMUNOTHERAPY | Anti-Tumor Antibodies
Targeting CA125 |
Oregovomab |
|---|---|---|
| Bispecific Antibodies
Targeting PD-1/LAG-3 |
Tebotelimab | |
| Cellular Therapy
Targeting MUC16Ecto |
4H11-28z/fIL-12/EFGRt+ CAR T | |
| Checkpoint Inhibitors
Targeting CD47, CTLA-4, PD-1, PD-L1, PVRIG, TIGIT |
Atezolizumab (Tecentriq™) Avelumab (Bavencio™) Balstilimab Botensilimab COM701 Dostarlimab (Jemperli™) Durvalumab (Imfinzi™) Ipilimumab (Yervoy™) Magrolimab Nivolumab (Opdivo™) ONC-392 Pembrolizumab (Keytruda™) Tislelizumab Tremelimumab Vibostolimab |
|
| Immune Cell Stimulators
Targeting IDO, IL-2R |
Epacadostat Nemvaleukin alfa |
|
| Vaccines
Targeting Tumor-associated Antigens, Survivin, TGFbeta, NY-ESO-1 |
DCVAC/OvCa Gemogenovatucel-T (FANG/Vigil™) Maveropepimut-S NY-ESO-1 |
| ONCOLYTIC VIRUSES | Oncolytic Viruses | MV-NIS Olvimulogene Nanivacirepvec |
|---|
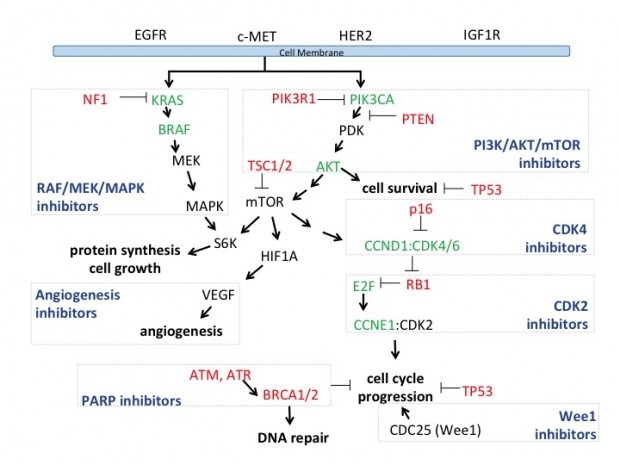
This diagram shows some of the key cell signaling pathways that are affected by genetic mutations or alterations found in ovarian cancers. The names of proteins encoded by the genes involved in various steps of each pathway are shown. Some proteins promote (indicated by an arrow) a particular step in the pathway and spur cell growth. Other proteins inhibit (indicated by the perpendicular symbol) a step in the pathway and prevent cells from growing and dividing in an uncontrolled way. Some genetic mutations/alterations result in a protein that is more active than it would normally be (shown in green), while others cause the protein to be less active (shown in red). A more active protein that stimulates cell growth or decreased activity of a protein that inhibits these processes can both lead to the uncontrolled growth seen in cancers.

